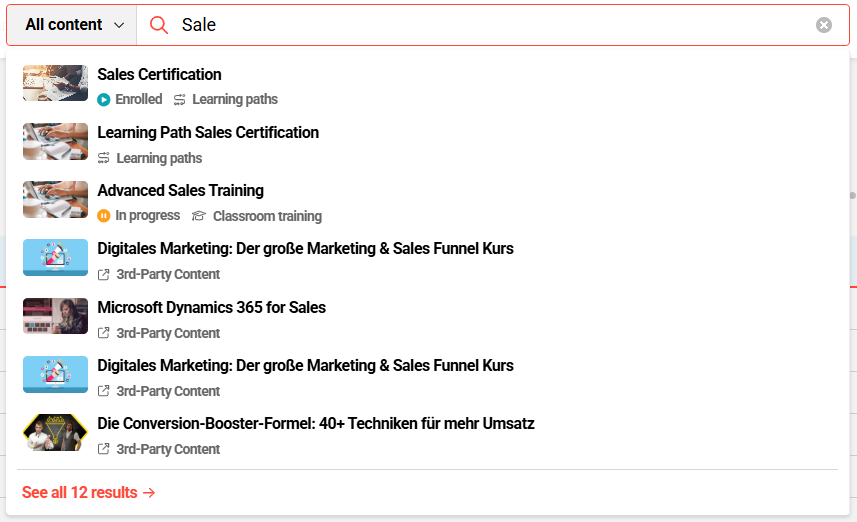

The global search is available for all customers with Kubernetes.
Overview and functionality
The global search helps users find learning content across catalogues, channels (if the add-on is in use) and personal learning content with a learning status (my learning area).
Please see details for what exactly is found and displayed as results here: Data Connector
The content search searches through titles, descriptions and (for lexical search also) keywording of channel media, courses, course templates, learning paths and learning path templates.
Please check the list of language analyzers to find out which languages are supported by Elasticsearch. If your language is not on the list, please contact imc to ask for options.
Triggered by the search query of the user the search finds content objects and ranks them according to their relevance. There are two ways to determine the relevance: a) lexical search (default setting, without AI) and b) semantic search (upon request, AI-enhanced).
Two search types: lexical vs. semantic search
The global content search is by default delivered to all customers with product version 14.25.1 and higher. Administrators can decide to make it visible to users or keep it hidden.
By default the lexical search type is used.
Lexical search
The word(s) in the user search query are matched with titles, keywords and descriptions of the indexed content. This method does not involve any AI.
Text preprocessing
-
tokenization (splits text into individual units (tokens), usually words or sub-words
-
lowercasing (converts all text to lowercase so capitialization does not affect matching)
-
removing stopwords (removes common words with little distinguishing value (e.g. “and”, “the”…)
-
stemming (reduces words to a common root so different grammatical forms can match)
Analysis techniques
-
Stem-based search reduces words to a common linguistic root (stem) so that different grammatical forms of the same word are matched during search.
Benefit: the search does not only find “running” but also “run” or “ran” -
edge-n-gram search (supported for product version ≥ 14.27.0.0)
An edge-n-gram is a character sequence of length “n” that is generated from the beginning (edge) of a word. Example: Word: “search” => 3-gram: “sea”, 4-gram: “sear”, 5-gram: “searc”….
Text is indexed as word prefixes and user queries are matched against these prefixes/fragments instead of full words. Edge-n-gram search is only applied to title and description. For keywords you assigned to content only the complete keyword is a match. (Keyword “Win10” does not match the query “Win100”)Benefits:
-
Results appear before a full word (stem) is typed, so n-grams bridge incomplete inputs
-
For queries that include an abbreviation (like “LMS”) no word stem or word meaning can be derived, but edge-n-grams enable partial and tolerant matching. It’s ideal for “search-as-you-type” experiences.
-
-
Fuzzy search (disabled for product version ≥ 14.27.1.0)
Fuzziness matches word that are similar in spelling, even if they are different words.
This technique was enabled up to product version 14.27.0.0 because it provided more tolerance for spelling mistakes. However customer experience showed that it blows up the result list and provides too many irrelevant results. With IP 14.27.1.0 it is therefore disabled.
Lexical search is recommended if…
-
your users mainly search by one or few keywords
-
your users often search for specific terms, abbreviations or numbers
-
your users expect to see the exact wording of their query in the top results (titles)
Semantic search
Semantic search uses AI-enhanced technology to interpret the intent and meaning behind user queries, as well as the content of the indexed data (currently: title and description). It understands natural language and compares the semantic meaning of the query with that of the learning content. This allows it to retrieve the most relevant or closely related information—even when different wording, phrasing, synonyms, or spelling variations are used.
This capability is powered by AI services provided by imc, including an embedding service that vectorizes both the indexed content and each user query. See Global Search for further information on how to require and activate semantic search.
How semantic search works:
-
Natural language precessing (NLP) and machine learning models are used to convert text into vectors that represent meaning.
-
The similarity of vectors between the user query and the indexed documents are compared to find the most relevant results.
-
For the vector representations, also called text embeddings, imc uses a self-hosted embedding model (jeffh) operated by Ollama.
Semantic search is recommended if…
-
your users often search for topic areas and wish to also find closely related content
-
your users sometimes struggle to find the exact search term that would match the wording that content creators use in the title.
-
your user queries and your content provide enough context for the semantic search to “work with”. Your course, learning path and media descriptions are well maintained and add background information to the title. The more input and context, the better the semantic search can be. The more information you provide, the better semantic search can interpret the meaning. Users can further improve the relevance of results by asking questions instead of using just a single search term.
If you are interested in using the semantic search type with AI services enabled for you, please read this https://doc-de.scheer-imc.com/ErsteSchritte/ki-gestutzte-inhaltssuche-compliance-informationen .
In summary:
If users want exact matches based on the characters they type in their query, lexical search is the right choice; if they want the system to understand meaning and tolerate different wording, semantic search is the better option.
Features & Benefits
-
Central entry point to content
The global search can be accessed from anywhere in the system, because it is located in the top navigation bar. The navigation search (mainly used by admins) can now be found behind an own icon. In the screenshot you see it next to the settings wheel.
-
Extended scope: Search within all catalogues, the channels and (with ≥14.27.1 also) within my learning
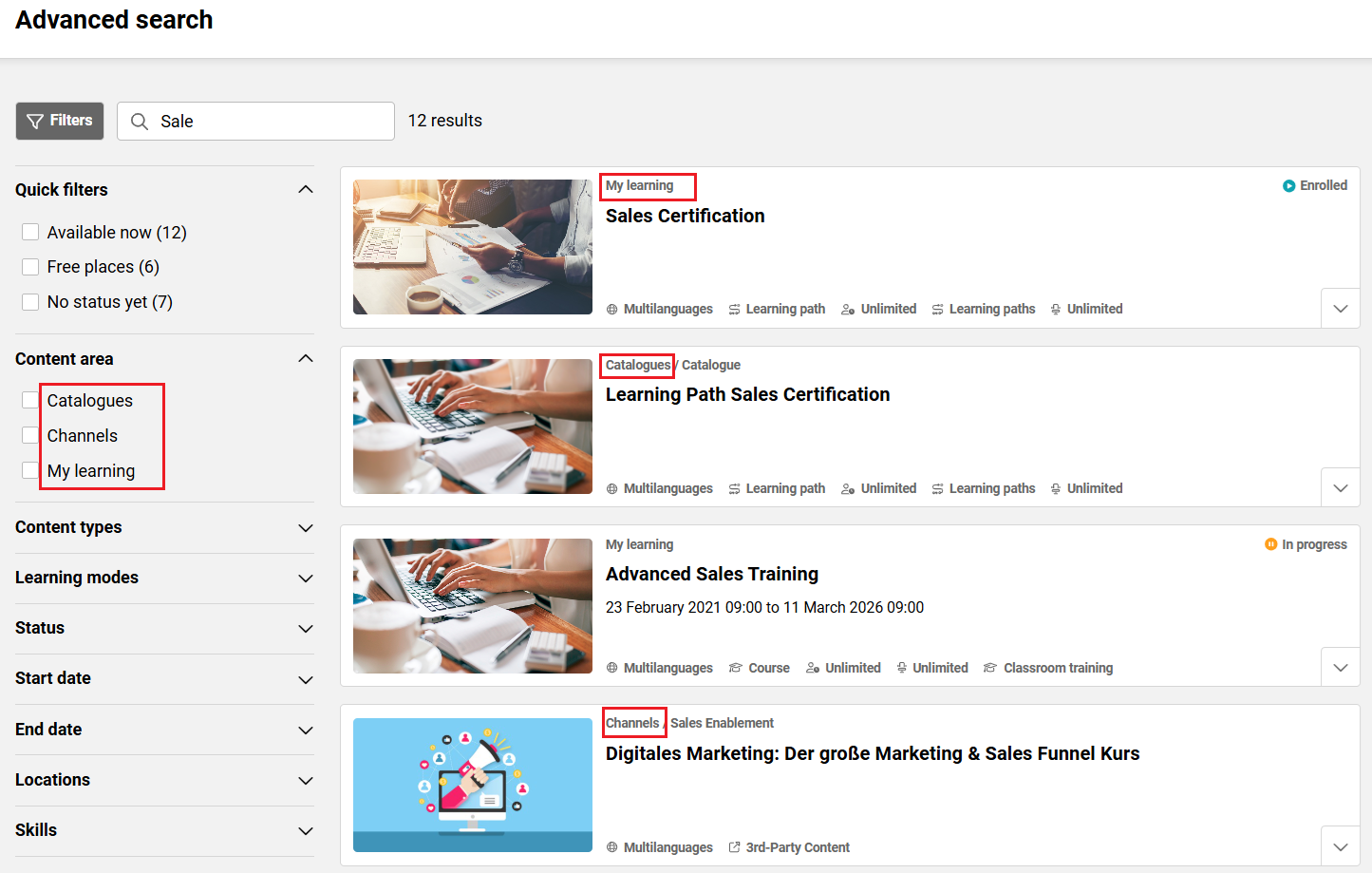
Customers with several content sources benefit from a comprehensive search across multiple areas: all catalogues, channels (add-on) and content with a personal learning status (my learning area) that might not be assigned to any catalogue. With the content area filter users can decide to search in all or in selected areas. The “content area” filter only appears for users with access to more than just one data source. -
Less clicks for a faster access to content
Once users start typing the top 7 results are displayed in a layer. This enables the user to access the top results without having to navigate to a search result page. -
Advanced search
If users decide they want to see all results they can navigate to the advanced search following the link “see all results”, or they press “enter”. The advanced search page enables users to apply filters, compare results by their descriptions and further criteria. -
New State-of-the-art search technology
ElasticSearch is a powerful, scalable, performant engine that supports multi-language and provides numerous possibilities to increase relevance and personalized results.
The search will be further enhanced and will be the basis for more AI features like the learner assistant.
Other searches in the system
-
Already existing content search bars like in the catalogues, in the my learning area or on panels are not affected by the global search. They are based on a different technology, search only within a page or area and will not be replaced by the global search and can exist in parallel.
-
Users with an overwhelming number of access points to content benefit from a simplified access via a central global search bar.
-
Please note: the navigation search (mainly for admins) that used to be in the top navigation will remain in the top navigation but it will be found behind a new icon:
Configuration & settings
First steps
The global search is included in the standard product for version ≥14.25.1.0 delivered as a lexical search . This does not include any AI.
Enable visibility and access to the search bar via navigation entry
-
To make the search visible in the top navigation you have to configure the navigation point for your user groups.
-
Go to “Navigation” and look for “platform_wide_search” to edit the access rights.

See https://doc-de.scheer-imc.com/FunkRef/search-configuration for more details.
Access to the search configurations
-
To make the search settings and data connector configuration accessible for your admins, go to “Navigation” and look for “data_connector_configuration”.

See https://doc-de.scheer-imc.com/FunkRef/search-configuration for more details.
After these changes logout and login again.
Configure the data connectors
imc uses a plugin approach, where each plugin represents a different area of learning content that is indexed to enable users to find content from that source. The plugins can be executed by the Data Connector, either time-based (as recurring or one-time jobs) or adhocly.
Learning content only becomes searchable after a successful initial job. The first job should be a full synchronisation, while each time further jobs run, new or updated content is added to the search index. Real-time indexing is not supported yet, but we plan to enable it in the future.
In the data connector configuration admins can
-
add or delete data plugins from the repository
-
configure these data plugins
-
schedule and maintain cron jobs to synch the search index with their data.
-
run an immediate synchronisation job independently of the schedule
The data plugins that allow you to search within your catalogs, channels and personal learning status are already added by default. Also by default, jobs have already been scheduled for to run daily in the night. You can trigger to run a job immediately without changing your regular schedule by clicking on the “Play”/”Execute now” button.
Please follow these instructions to configure plugins: https://doc-de.scheer-imc.com/FunkRef/data-connector-configuration .
Define and check on the jobs
For each job listed here, you can define a certain schedule. Use the 3-dots menue button on the right (hover) to edit the jobs.
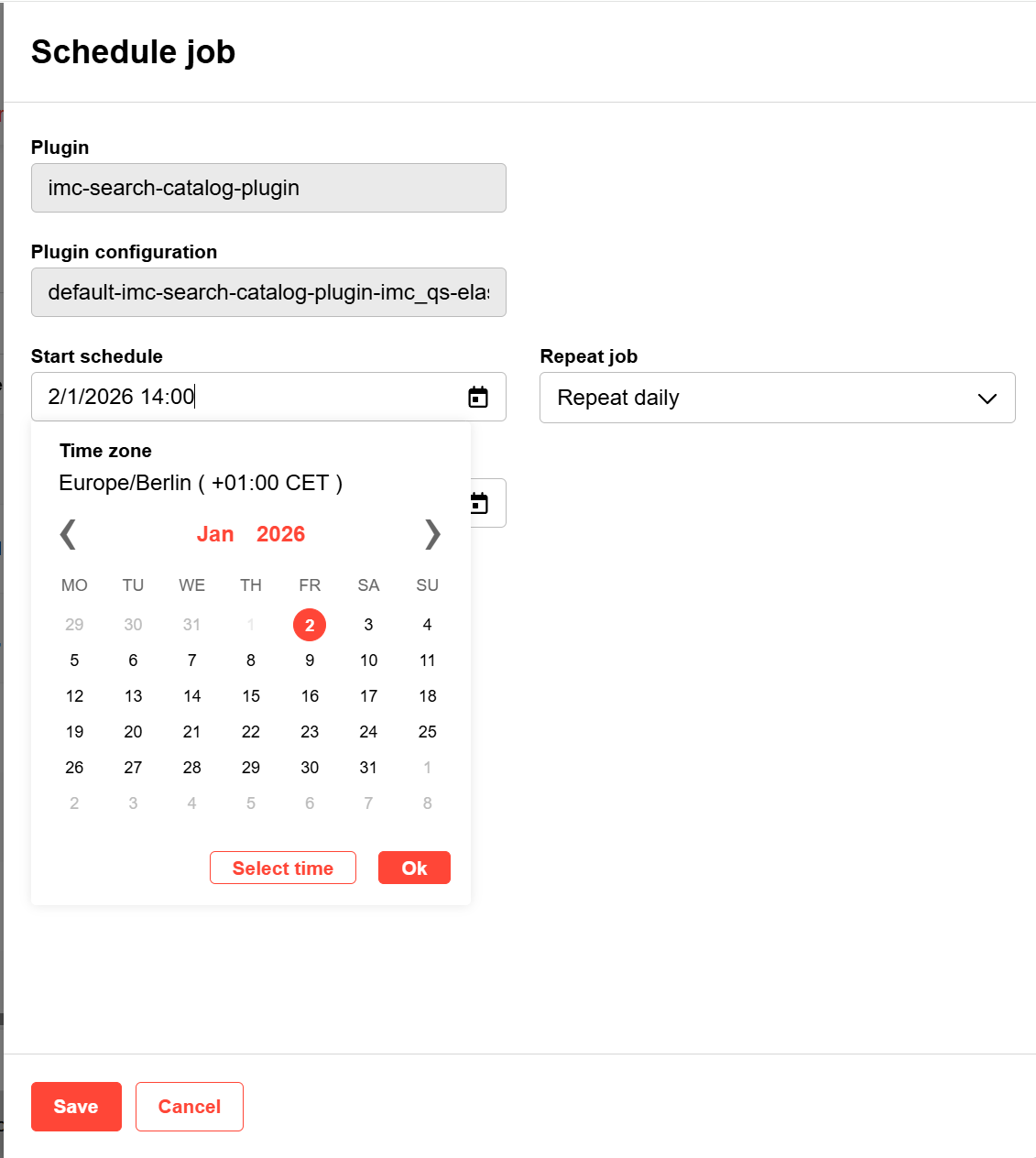
The columns on this page provide you with the following information:
Job: Name of the job that synchronises the search index with your data
Configuration: Name of the configuration of the job
Plugin: Name of plugin representing a data source connected (e.g. channels, catalogs or “context” meaning “My Learning” content)
Latest execution: shows the date and time when the last job ended
Latest status: shows the status of the latest executed job
Activate schedule: if you define a date and time for a future job (recurring or one time) the schedule is automatically switched on, but you can switch it off manually if you wish to pause the defined schedule.
Recurring: shows if the job runs in a defined frequency always at the defined time (“Yes”) or if it only runs/ran once (“No”)
Next execution time: show the date and time when the next job will start. If it is empty, no future job is scheduled.
Please note if the job for the channel plugin fails, the issue might be lying with service account user (see the blue info box). If a job fails you can download the log files to check what went wrong.
Optional steps
Switch to AI-enhanced semantic search
If you wish to enable semantic search for your users, imc needs to make AI services available for you.
-
Before you decide for an AI-enhanced, semantic search please confirm you have read and agree to the https://doc-en.scheer-imc.com/GettingStarted/ai-enhanced-content-search-compliance-information
-
Please contact the imc Service Helpdesk to request these services to be deployed without extra costs.
-
As soon as the services are available you can activate semantic search in the search settings.
Go to “Configuration” > “Search settings”, 2. tab “Global search” and switch the “Active search type” to “semantic search”.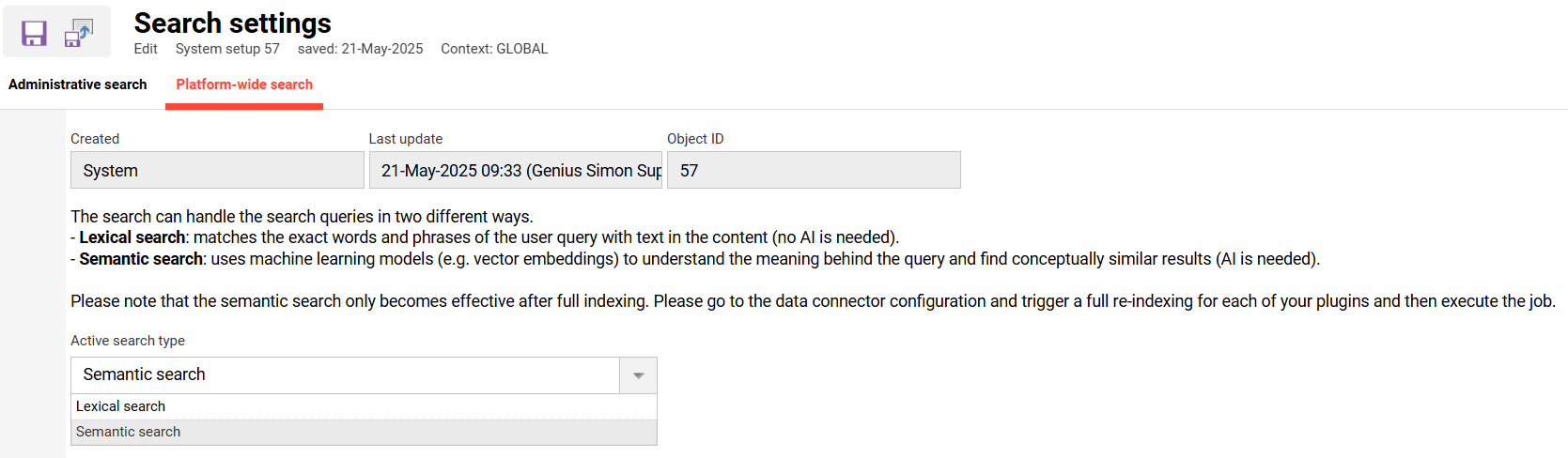
-
Please note: A switch requires another full indexing of your data. The embedding service has to create vectors for all content to better interpret its meaning.

-
Go to the data connector configuration to request a full synch of the search index with the next job.
-
In the data connector configuration go to the second tab “Configurations”, look for “Catalog Plugin Fetch Properties” and type in a “0” in the field “Number of days to sync back”.
-
We advice to do this full-synch outside of working hours as it might take some time (depending on your data volume) and might affect the user search experience for simultaneous search requests. We also recommend to change the setting “0” back to your preferred period for future synchronisations, as a full synch might not be needed every time afterwards.
-
Please see Configuration Manager - Search Settings for more details.
If for some reason you want to revoke your decision about the search type you can change back to lexical search in the search settings.
Customize the wording on the user interface
You might have chosen your own corporate wording for “Catalogue” or “Channels” or “My learning”.
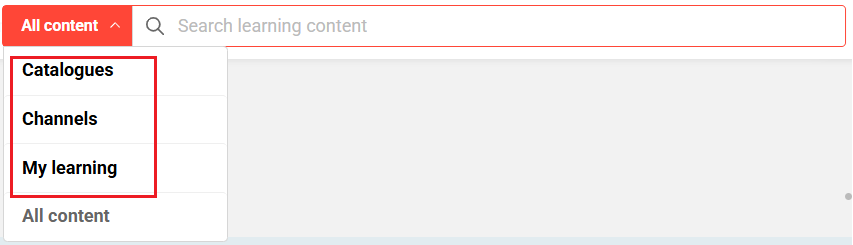
If your users are not familiar with the default terms imc uses in the search user interface, because you call them differently in your system (e.g. “learning offer”) you can change the wording in the “system texts”.
Following are the bundle names for Catalogue, Channels, Course Templates and “My learning” which can be updated to reflect the custom wording. Please note these bundles are global search specific and would only impact global search.
-
Catalogue -> strPlatformSearchContentCatalog
-
Channels -> strPlatformSearchContentChannels
-
Course Templates -> strPlatformSearchContentCourseTemplates
-
My Learning-> strPlatformSearchContentLearningStatus
The default wording for the plugins and data sources is “imc-search-context-plugin” for “My learning” plugin, “imc-search-catalog-plugin” for catalogue plugin and “imc-search-plugin-channels” for channels plugin and cannot be changed.
Guidelines & Recommendations
We have summarized some tips for the usage of AI-enhanced content search : Recommendations for the Use of the Global Search
